<div>
<h2>How AI is Revolutionizing Go-to-Market Strategies for Startups</h2>
<p id="speakable-summary" class="wp-block-paragraph">For years, startups relied on traditional sales playbooks, but the rise of AI is reshaping how companies approach their market launch.</p>
<h3>Max Altschuler on Doing More with Less</h3>
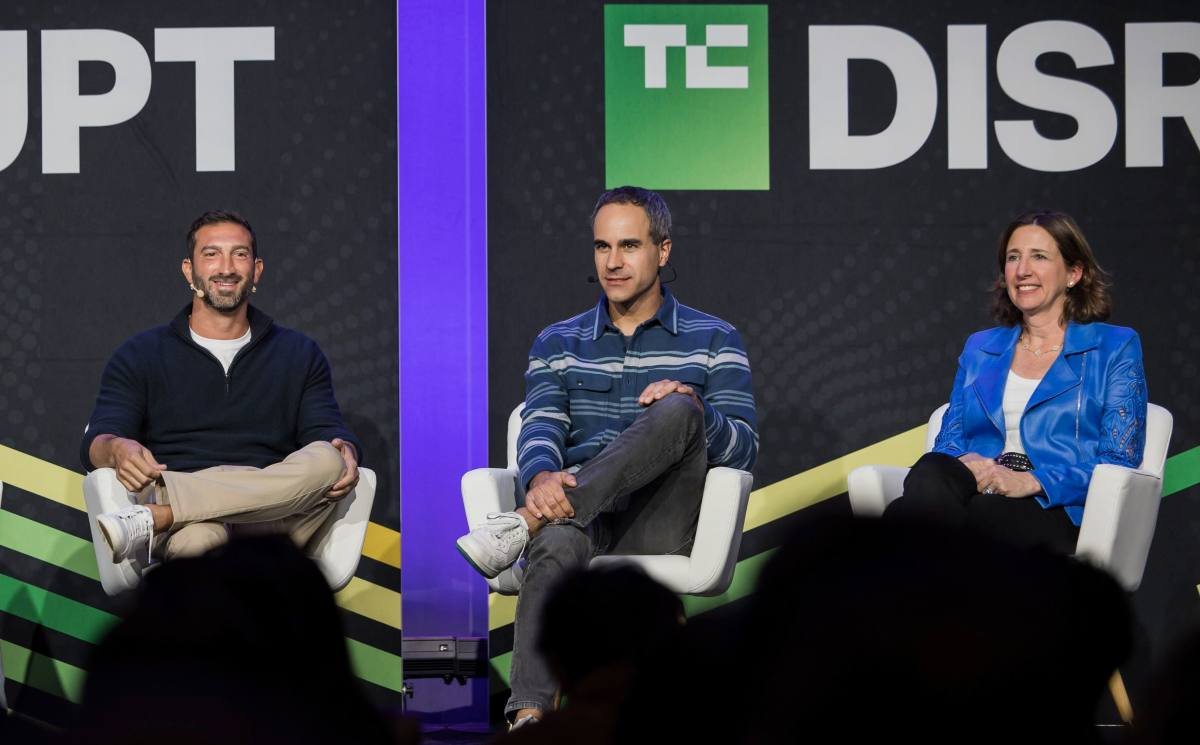
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“You can do more with less than ever before,” said <a target="_blank" rel="nofollow" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/maxaltschuler/">Max Altschuler</a>, general partner at GTMfund, during his presentation at <a target="_blank" href="https://techcrunch.com/events/tc-disrupt-2025/">TechCrunch Disrupt</a> last month.</p>
<h3>Navigating New Challenges in GTM Approaches</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">However, founders must be careful. While some startups are hiring developers to tackle common GTM issues, Altschuler emphasized the continued importance of having specific domain expertise.</p>
<h3>The Value of Knowledgeable Advisors</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“Having great advisors allows you to leverage tried-and-true playbooks. These principles still apply. A solid understanding of marketing fundamentals is essential,” Altschuler noted.</p>
<h3>Alison Wagonfeld on the Enduring Craft of Marketing</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph"><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/alisonwagonfeld/">Alison Wagonfeld</a>, VP of Marketing at Google Cloud, affirmed that marketing skills remain crucial.</p>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“AI knowledge and curiosity are important, but understanding customer insights, conducting research, and recognizing effective creativity are vital components of marketing,” Wagonfeld stated.</p>
<h3>The Speed of AI-Driven Teams</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Teams that integrate AI technologies can operate more swiftly. “You can communicate more messages in less time and consider the metrics you're driving,” she added.</p>
<div class="wp-block-techcrunch-inline-cta">
<div class="inline-cta__wrapper">
<p>Join us at the TechCrunch event</p>
<div class="inline-cta__content">
<p>
<span class="inline-cta__location">San Francisco</span>
<span class="inline-cta__separator">|</span>
<span class="inline-cta__date">October 13-15, 2026</span>
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<h3>Marc Manara on AI and Strategic Focus</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph"><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/marcmanara/">Marc Manara</a>, head of startups at OpenAI, noted that startups are increasingly incorporating AI into their GTM strategies, but not solely to reduce resources.</p>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“The focus is now on how to execute effectively. AI allows for highly personalized engagements and advanced data analysis,” he said. “The sophistication of lead generation tools has evolved significantly.”</p>
<h3>Enhancing Inbound Marketing Precision</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">According to Manara, inbound marketing has also transformed, utilizing AI-driven insights for more accurate qualification and scoring of leads compared to the past.</p>
<h3>Rethinking Team Composition for GTM Success</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">As startups craft their go-to-market strategies, Wagonfeld emphasized the need for teams that exhibit curiosity and understanding rather than simply hiring specialists with niche expertise.</p>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“Today, hiring for a sense of curiosity and adaptability is paramount,” she concluded. “These qualities are now key for building effective GTM teams.”</p>
</div>This revised version emphasizes critical points and improves readability while maintaining a structured HTML format to enhance SEO.
Here are five FAQs regarding how OpenAI and Google perceive AI’s impact on go-to-market strategies:
FAQ 1: How is AI influencing product development in go-to-market strategies?
Answer: AI enables companies to gather and analyze vast amounts of data, leading to more informed product development. By identifying consumer preferences and market trends through predictive analytics, businesses can tailor products to better meet customer needs, resulting in a more effective go-to-market strategy.
FAQ 2: What role does AI play in customer segmentation?
Answer: AI helps businesses segment their customer base with precision by analyzing behavioral data, demographics, and purchasing patterns. This allows companies to create targeted marketing campaigns, improving engagement and conversion rates while optimizing resources.
FAQ 3: How do OpenAI and Google view AI’s impact on sales forecasting?
Answer: Both OpenAI and Google highlight that AI enhances sales forecasting accuracy through machine learning algorithms that analyze historical sales data and market conditions. This predictive capability allows companies to make better inventory and resource management decisions, ultimately driving sales growth.
FAQ 4: In what ways can AI streamline customer interactions in go-to-market strategies?
Answer: AI can improve customer interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants, providing real-time support and personalized experiences. This capability not only enhances customer satisfaction but also frees up human resources to focus on more complex inquiries, leading to a more efficient go-to-market approach.
FAQ 5: What challenges do companies face when integrating AI into their go-to-market strategies?
Answer: Companies may encounter challenges like data privacy concerns, integration of AI systems with existing workflows, and the need for upskilling employees. It’s crucial for organizations to address these issues to fully leverage AI’s potential in their go-to-market strategies.