Adobe Firefly Revolutionizes AI Video Editing with New Features
Adobe is enhancing its AI video-generation platform, Firefly, by introducing an innovative video editor that facilitates precise prompt-based edits. This update also incorporates new third-party models for image and video generation, notably Black Forest Labs’ FLUX.2 and Topaz Astra.
Streamlined Editing with Prompt-Based Controls
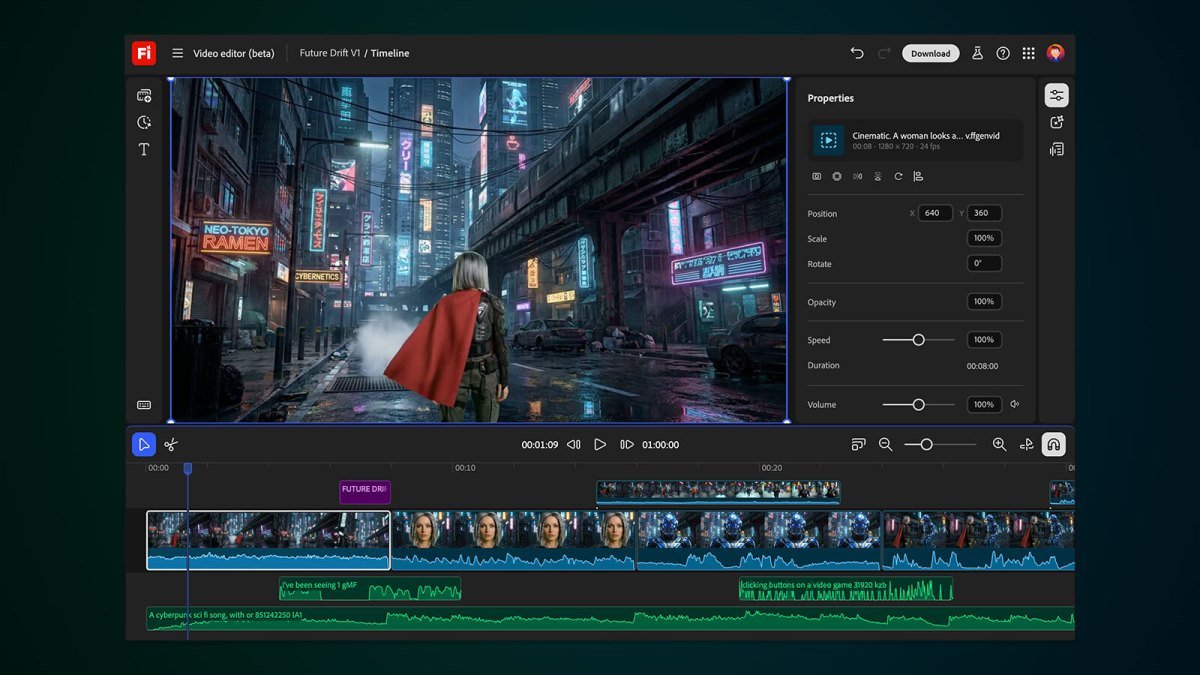
Previously, Firefly limited users to full clip recreation if any aspect was unsatisfactory. The newly launched editor allows for text prompts to refine video elements, adjusting colors, camera angles, and more. Users can now easily manipulate frames, audio, and other features through an intuitive timeline view.
Introducing New Models and Features
Initially announced in October as a private beta, the video editor is now accessible to all users. With the integration of Runway’s Aleph model, creators can provide specific instructions such as “Change the sky to overcast and lower the contrast” or “Zoom in slightly on the main subject.”
Advanced Camera Manipulation and Upscaling Capabilities
Users can leverage Adobe’s own Firefly Video model to upload a starting frame and a reference video to recreate desired camera angles. Additionally, the Topaz Labs’ Astra model enables video upscaling to 1080p or 4K, while FLUX.2 will enhance image generation capabilities in the app. Moreover, a collaborative boards feature will be introduced soon.
Immediate Availability and Future Releases
FLUX.2 is now available across all platforms within Firefly, with Adobe Express users gaining access starting in January. Adobe seeks to engage more users by continually improving Firefly amid competition in image and video generation tools.
Special Offers for Firefly Subscribers
To attract users, Adobe will provide unlimited generations from all image models, including the Firefly Video Model, to subscribers of Firefly Pro, Firefly Premium, and certain credit plans until January 15.
A Year of Transformative Updates
Adobe has significantly revamped Firefly this year, launching subscriptions for varied image and video generation levels, followed by a new Firefly web app and mobile applications, alongside enhanced support for additional third-party models.
Here are five FAQs regarding Adobe Firefly’s new features:
FAQ 1: What is prompt-based video editing in Adobe Firefly?
Answer: Prompt-based video editing allows users to generate and modify video content using natural language prompts. This means you can describe what you want to see in the video, and Adobe Firefly will assist in creating or editing the footage accordingly.
FAQ 2: How does the addition of third-party models enhance Adobe Firefly’s capabilities?
Answer: The integration of third-party models expands the range of creative possibilities by allowing users access to diverse AI tools and resources. This helps in generating more customized and varied content tailored to specific needs or styles.
FAQ 3: What types of video editing tasks can I perform using Adobe Firefly’s prompt-based features?
Answer: You can perform a variety of tasks, including scene alterations, adding visual effects, color grading, and more—simply by inputting descriptive prompts. This aims to streamline the editing process and make it more intuitive.
FAQ 4: Is there a learning curve for using these new features in Adobe Firefly?
Answer: While there might be an initial adjustment period, Adobe Firefly is designed with user-friendliness in mind. Many find that using prompts simplifies tasks, making it accessible even for those with limited video editing experience.
FAQ 5: Are there any additional costs associated with using third-party models in Adobe Firefly?
Answer: The pricing structure for using third-party models may vary based on the specific models or services being utilized. It’s best to check Adobe’s official documentation or pricing page for the latest information on any additional costs.