<div>
<h2>Google Partners with Airtel to Combat Spam in India's RCS Messaging Ecosystem</h2>
<p id="speakable-summary" class="wp-block-paragraph">Facing persistent spam issues in India's Rich Communication Services (RCS) platform, Google is enhancing its defenses through deeper carrier integration.</p>
<h3>Strengthening Spam Protections with Airtel</h3>
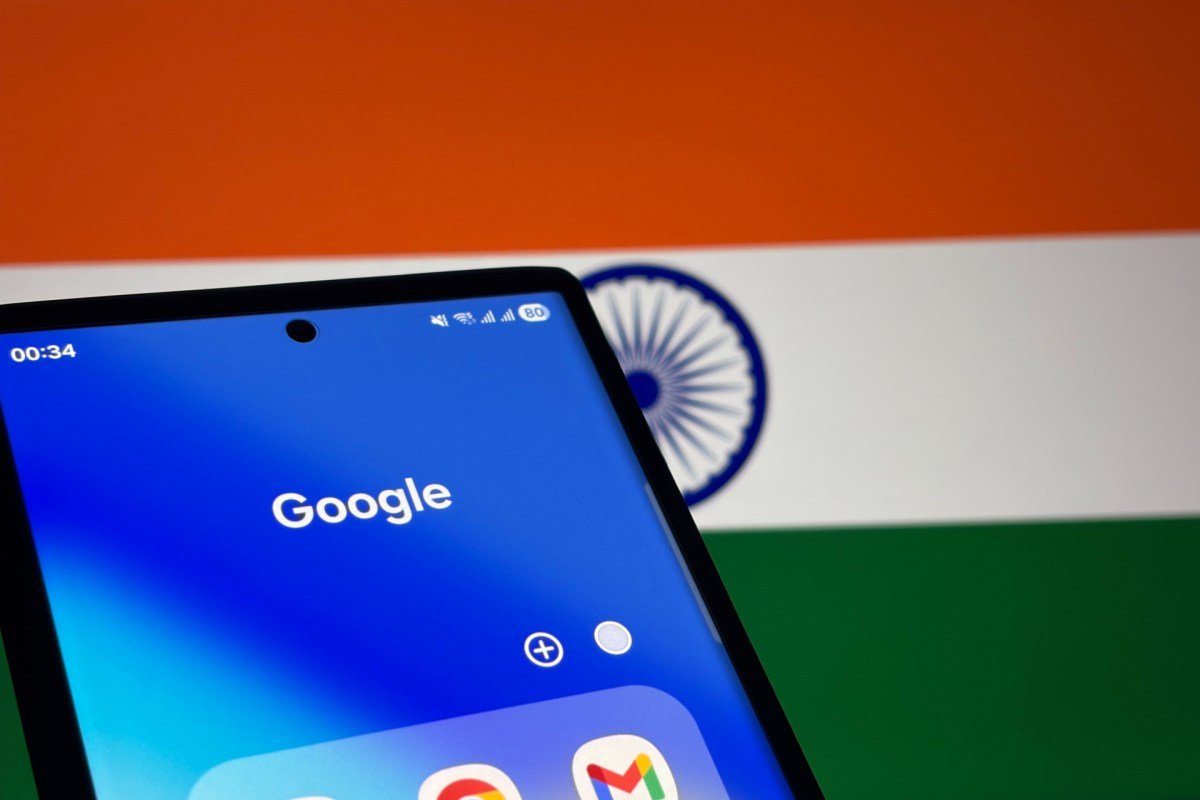
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">In a significant development, Bharti Airtel, India’s second-largest telecom provider with over 463 million subscribers, has joined forces with Google to integrate network-level spam filtering into India's RCS framework. This collaboration aims to bolster protections against unwanted messages and fraudulent activities on the platform.</p>
<h3>Addressing India's Spam Challenge</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">India is a particularly challenging market for spam and fraud, attributed to its large mobile user base, rapid growth in digital transactions, and aggressive marketing practices. In 2022, the volume of spam complaints on Google’s RCS, mostly via the Google Messages app, led the company to temporarily halt business promotions due to overwhelming user dissatisfaction.</p>
<h3>Airtel's Cautious Approach</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Airtel was hesitant to fully integrate with Google’s RCS until it ensured traffic was routed through its spam control systems, highlighting concerns about increasing fraud risks. An Airtel spokesperson stated, “We had not onboarded Google because we first wanted RCS messages to be routed through the Airtel spam filter.”</p>
<h3>Innovative Spam Filtering Features</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">The partnership will leverage Airtel’s network intelligence along with Google’s RCS platform to implement real-time checks on business messaging. These features will include sender verification, spam detection, and the enforcement of users' do-not-disturb preferences. Airtel has dubbed this integration as a “global first,” although comparisons with existing systems were not disclosed.</p>
<h3>Google's Commitment to Global Messaging Security</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">“We are dedicated to collaborating with the broader ecosystem of carriers to ensure a consistent and trustworthy messaging experience for RCS users worldwide,” said Sameer Samat, president of the Android ecosystem at Google. His comments suggest a potential extension of this model beyond India to standardize security across the RCS landscape.</p>
<h3>The Importance of India in Google's Messaging Strategy</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">India is crucial to Google’s messaging strategies, boasting more than a billion internet users and over 700 million smartphone users. Additionally, it has over 853 million WhatsApp users, emphasizing fierce competition in the mobile messaging sector.</p>
<h3>Industry Insights on Carrier Integration</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Prabhu Ram, vice president of industry research at CyberMedia Research, stated that deeper carrier integration aims to address long-standing vulnerabilities in rich messaging ecosystems prone to spam and fraud. "The efficacy of this partnership should be measured by reductions in spam volume, user complaints, and fraud occurrences, alongside improvements in engagement with legitimate messages," he told TechCrunch.</p>
<h3>Airtel's Anti-Spam Efforts</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Airtel has ramped up its anti-spam initiatives over the past year, employing AI-driven systems that have blocked over 71 billion spam calls and 2.9 billion spam messages, resulting in a nearly 69% decrease in fraud-related losses on its network.</p>
<h3>Google's Vision for RCS as the Future of Messaging</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">On a broader scale, Google is positioning RCS as the successor to SMS, recently announcing that RCS currently handles more than a billion messages daily in the U.S., based on a 28-day average.</p>
<h3>Future Prospects for Carrier Integrations</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Google has yet to confirm whether similar carrier integrations will be rolled out in other regions or provide estimates on how effectively this initiative could mitigate spam and fraud.</p>
</div>This rewritten article maintains the original information while improving SEO structure, ensuring engaging headlines, and formatting for web presentation.
Here are five FAQs regarding Google’s efforts to tackle RCS spam in India:
FAQ 1: What is RCS, and why is it important for messaging in India?
Answer: RCS, or Rich Communication Services, is an advanced messaging protocol designed to enhance SMS with features like read receipts, group chats, and high-resolution media sharing. In India, where messaging is a primary communication tool, RCS aims to provide a richer experience while addressing issues like spam.
FAQ 2: What specific measures is Google implementing to combat RCS spam in India?
Answer: Google plans to enhance spam detection and reporting systems for RCS messages. This includes leveraging machine learning to identify and filter spam messages more effectively, improving user experience, and ensuring that legitimate communications are prioritized.
FAQ 3: How can users in India report RCS spam messages?
Answer: Users can report spam messages directly through their messaging app. Typically, there will be an option to mark messages as spam, which will then be analyzed by Google’s systems to improve spam detection and mitigate future spam incidents.
FAQ 4: Will this initiative require collaboration with mobile carriers in India?
Answer: Yes, Google’s initiative to tackle RCS spam will involve collaboration with mobile carriers. By working together, they can share insights, data, and resources to implement effective spam prevention measures across networks.
FAQ 5: How will these changes improve the overall messaging experience for users?
Answer: By reducing RCS spam, users will experience less clutter in their messaging apps, leading to easier and more efficient communication. Improved spam detection will also help ensure that important messages are not overlooked, thereby enhancing user confidence in using RCS for personal and business communications.