<div>
<h2>The Evolving Landscape of AI Startup Investments</h2>
<p id="speakable-summary" class="wp-block-paragraph">Venture capitalists recognize that investing in AI startups demands a novel approach, distinct from previous tech innovations.</p>
<h3>A New Investment Paradigm for AI</h3>
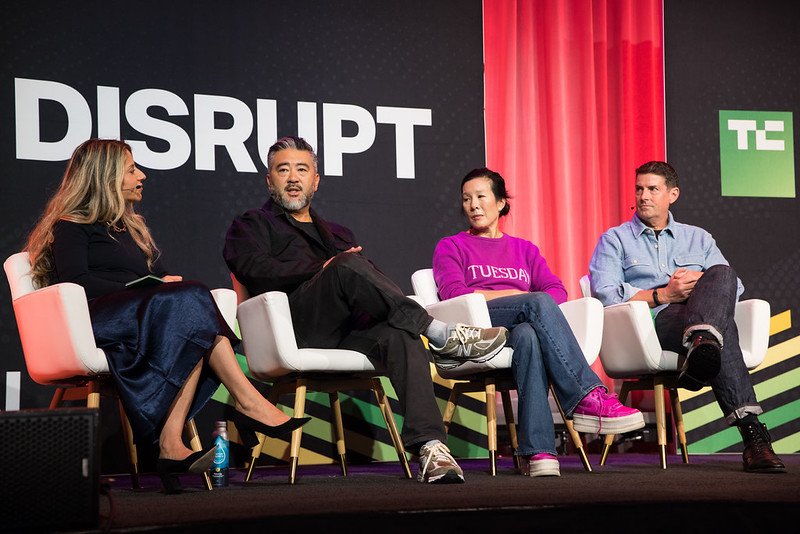
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">"It’s a funky time," remarked Aileen Lee, founder and managing partner of Cowboy Ventures, during her appearance at TechCrunch Disrupt 2025. She emphasized that the rules of engagement have transformed, as some AI companies achieve "zero to $100 million in revenue within a single year."</p>
<h3>What Investors Are Really Looking For</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Lee highlighted that Series A investors aren't merely focused on explosive revenue growth. "It’s an algorithm with different variables and different coefficients," she explained, detailing how aspects like data generation, competitive strength, founders' track records, and product technicality are measured.</p>
<h3>Challenges in Securing Follow-On Funding</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Jon McNeill, co-founder and CEO of DVx Ventures, noted that even startups achieving rapid growth to $5 million often struggle to secure subsequent funding. "This game has changed, and it is changing dynamically," he asserted.</p>
<h3>Raising the Bar for Seed-Stage Startups</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">McNeill pointed out that investors are now applying rigorous criteria to seed-stage companies that were previously reserved for more mature entities. "Breakout companies often don’t have the best tech," he said, stressing that successful startups focus on effective go-to-market strategies.</p>
<h3>The Balancing Act: Technology vs. Go-to-Market Strategy</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Steve Jang, founder of Kindred Ventures, contested the notion that a great go-to-market strategy outweighs technological prowess. "It’s not entirely accurate to claim that mediocre tech can triumph purely with strong marketing," he stated, reinforcing the need for a dual focus.</p>
<h3>Marketing Sophistication is Key</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">McNeill later clarified that while a solid product is crucial, founders must prioritize building robust sales and marketing strategies from the outset. "Investors are becoming more sophisticated in evaluating go-to-market approaches," he said.</p>
<h3>The Pressure to Innovate Rapidly</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Lee mentioned that AI startups face unprecedented pressure to roll out product updates and features rapidly, preempting competitors. "If you look at OpenAI and Anthropic, you’ll need to match their pace and quality," she advised.</p>
<h3>The AI Landscape: A Work in Progress</h3>
<p class="wp-block-paragraph">Despite these pressures, panelists unanimously acknowledged that the AI sector remains in its infancy. As Jang put it, "There are no clear winners, even among LLMs. Competitors are right on their heels." This presents opportunities for new players to challenge established leaders.</p>
</div>This structure maintains the original content’s essence while enhancing readability and SEO optimization with well-structured headings.
Here are five FAQs related to the trend of VCs abandoning old rules for a more unconventional approach to investing in AI startups:
FAQ 1: What does it mean for VCs to abandon old rules in investing?
Answer: Abandoning old rules means that venture capitalists are moving away from traditional investment strategies and criteria, such as extensive market research and revenue forecasts. Instead, they are embracing a more open-minded approach, focusing on the potential of innovative ideas, unique technologies, and the creative vision of startup founders.
FAQ 2: Why are VCs investing in AI startups now more than ever?
Answer: The surge in AI innovations and applications has created exciting opportunities for growth. VCs recognize that AI is transforming industries, and investing early in these technologies can lead to substantial returns. The increasing demand for AI solutions in various sectors makes this a promising area for investment.
FAQ 3: What kind of startups are attracting VC attention in the AI sector?
Answer: Startups that demonstrate not only advanced technology but also creative and unconventional business models are gaining traction. VCs are particularly interested in companies that leverage AI in unique ways, such as improving user experience, automating complex processes, or creating entirely new markets.
FAQ 4: How can startups best position themselves to attract VC funding in this new investment climate?
Answer: Startups should focus on showcasing their innovative potential and scalability. Building a compelling narrative around the technology, its applications, and the team behind it can help. Additionally, demonstrating adaptability and responding to market changes quickly can resonate with VCs looking for future-proof investments.
FAQ 5: What are the risks of this new ‘funky’ approach to investing?
Answer: While this unconventional approach can lead to high rewards, it also comes with risks. VCs may invest in startups without the extensive due diligence traditionally required, which could result in funding unreliable or underperforming companies. Additionally, the rapid pace of change in the AI sector means that today’s hot technology might become obsolete quickly, adding further investment risk.