California’s Landmark AI Safety Bill Receives Final Approval
In a significant move for AI governance, California’s state senate approved a critical AI safety bill early Saturday morning, imposing new transparency mandates on large technology firms.
Key Features of SB 53
The bill, championed by state senator Scott Wiener, introduces several pivotal measures. According to Wiener, SB 53 mandates that large AI laboratories disclose their safety protocols, offers whistleblower protections for employees, and initiates a public cloud service called CalCompute to broaden computing access.
Next Steps: Governor Newsom’s Decision
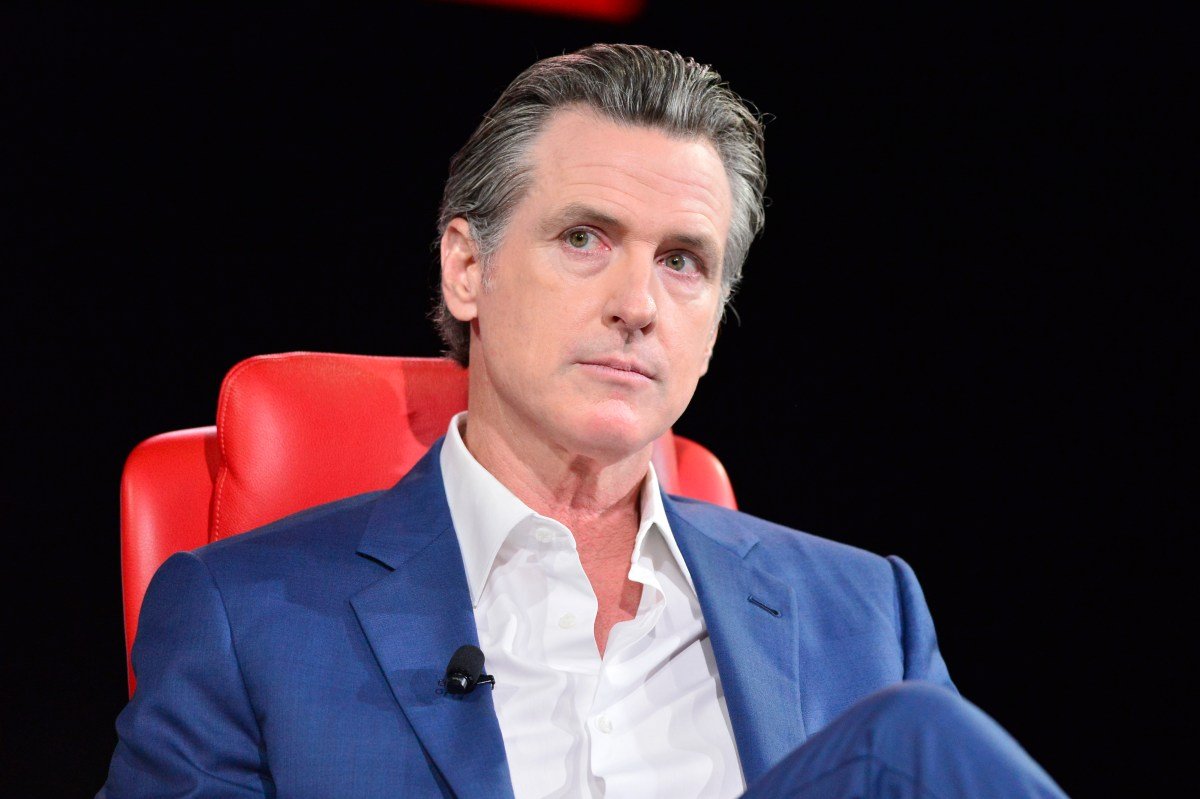
The bill is now on Governor Gavin Newsom’s desk for signature or veto. While he has yet to comment on SB 53, he notably vetoed a previous, more extensive safety bill by Wiener last year, despite endorsing narrower legislation addressing issues like deepfakes.
Governor’s Previous Concerns and Influences on Current Bill
In his earlier decision, Newsom acknowledged the necessity of “protecting the public from genuine threats posed by AI,” but criticized the stringent standards proposed for large models, questioning their applicability outside high-risk environments. This new legislation has been reshaped based on recommendations from AI policy experts assembled by Newsom post-veto.
Amendments: Streamlining Expectations for Businesses
Recent amendments to the bill now dictate that companies developing “frontier” AI models with annual revenues below $500 million will need only to disclose basic safety information, while those exceeding that revenue threshold must provide detailed reports.
Industry Pushback and Calls for Federal Standards
The proposal has faced opposition from various Silicon Valley companies, venture capital firms, and lobbying groups. In a recent correspondence to Newsom, OpenAI argued for a harmonized approach, suggesting that companies meeting federal or European standards should automatically be compliant with California’s safety regulations.
Legal Concerns About State Regulation
The head of AI policy at Andreessen Horowitz has cautioned that many state-level AI regulations, including proposals in California and New York, may violate constitutional restrictions on interstate commerce. The co-founders of a16z have cited tech regulation as one of the reasons for their support of Donald Trump’s campaign for a second term, leading to calls for a 10-year ban on state AI regulations.
Support from the AI Community
In contrast, Anthropic has publicly supported SB 53. Co-founder Jack Clark stated, “While we would prefer a federal standard, in its absence, this bill establishes a robust framework for AI governance that cannot be overlooked.” Their endorsement highlights the importance of this legislative effort.
Here are five FAQs regarding California’s AI safety bill SB 53, along with their answers:
FAQ 1: What is California’s AI safety bill SB 53?
Answer: California’s AI safety bill SB 53 aims to establish regulations surrounding the use and development of artificial intelligence technologies. It emphasizes ensuring safety, accountability, and transparency in AI systems to protect consumers and promote ethical practices in the tech industry.
FAQ 2: What are the key provisions of SB 53?
Answer: Key provisions of SB 53 include requirements for AI developers to conduct risk assessments, implement safety measures, and maintain transparency about how AI systems operate. It also encourages the establishment of a framework for ongoing monitoring of AI technologies’ impacts.
FAQ 3: Why is Governor Newsom’s approval important for SB 53?
Answer: Governor Newsom’s approval is crucial because he has the power to veto the bill. If he issues a veto, the bill will not become law, meaning the proposed regulations for AI safety would not be enacted, potentially leaving gaps in consumer protection.
FAQ 4: How does SB 53 address potential risks associated with AI?
Answer: SB 53 addresses potential risks by requiring developers to evaluate the impacts of their AI systems before deployment, ensuring that they assess any hazards related to safety, discrimination, or privacy. This proactive approach aims to mitigate issues before they arise.
FAQ 5: What happens if Governor Newsom vetoes SB 53?
Answer: If Governor Newsom vetoes SB 53, the bill would not become law, and the current regulatory framework governing AI would remain in place. Advocates for AI safety may push for future legislation or modifications to address prevailing concerns in the absence of the bill’s protections.